This post is about how Square makes money. Firstly, we explain the key elements of Square business model. We provide information on Square products and services, customers, revenue sources, and key cost elements. Then, we share Square Gross Payments Volume (GPV) analysis for the year 2015. Then, we share the revenues, the profits, and the profit margins of Square for 2015.
Key Elements Of Square Business Model
Square, Inc. (“SQ”) is a credit card processing and business solutions provider. Square provides free software app with affordable hardware (which is often free) that turn mobile devices into powerful point-of-sale (POS) solutions. This helps sellers or merchants with a mobile device to accept card payments, anywhere, anytime. Square also enables sellers to receive payments made through EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) chip cards and latest contactless payment methods (such as Apple Pay) that are based on near-field communications (NFC) technology. Square makes it easy for sellers to get started in minutes and requires no credit checks. Square offers same rate for the acceptance of Visa, MasterCard, Discover, and American Express payment cards.
Square acts as a payment service provider. Square holds the direct relationship with the sellers and facilitates the payment transaction, on behalf of the seller, with the payment card networks and banks. Sellers do not need to deal with the complex systems, rules, and requirements of the payment industry. Square acts as a merchant of record for its sellers. This puts the risk for refunds and chargebacks on Square.
Square Products And Services
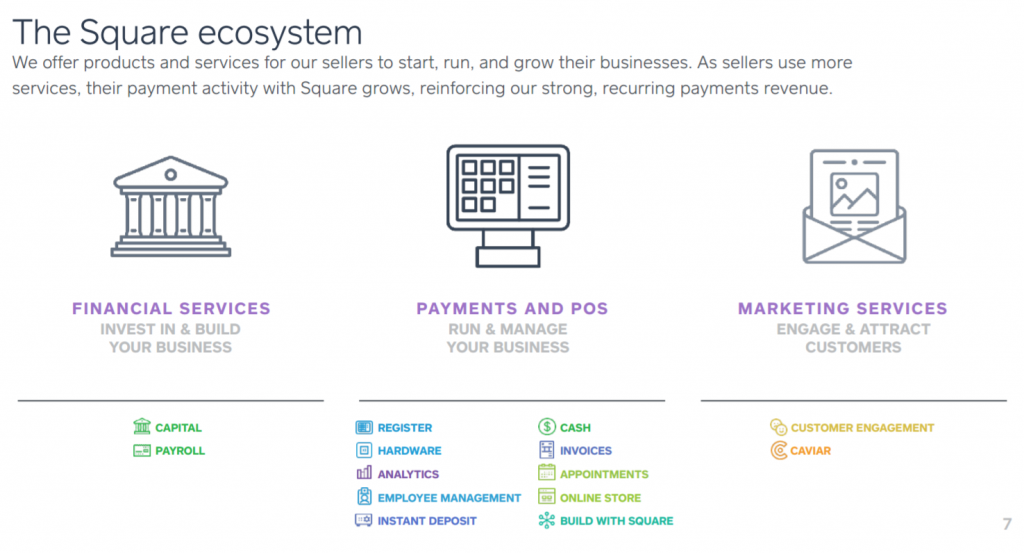
Square products and services are organized in three categories:
- Payments and POS Services. These include hardware and software solutions to accept payments in-person or online and analyze business information.
- Financial Services. These help sellers with funds to run and grow their businesses.
- Marketing Services. These help sellers reach their customers and increase sales.
Square Payments and POS services business offerings include:
- Square Readers. Square offers different kinds of card readers to help accept credit cards securely. All of them work with Square Register mobile app to form a simple POS solution
- Square Magstripe Reader plugs into the standard headset jack of a mobile device and enables sellers to accept payments by swiping a buyer’s payment card.
- Square Reader for EMV chip cards also plug into the standard headset jack of a mobile device. It enables sellers to accept payments by dipping the EMV chip or swiping the stripe.
- Square Reader for EMV Chip Cards and NFC connects wirelessly to mobile devices. In enables sellers to accept contactless payments that are made via the tap of the buyer’s mobile device using NFC. This enables sellers to accept via Apple Pay, Android Pay, and other mobile wallets.
- Square Stand transforms an iPad into a full POS terminal. It features an integrated magnetic stripe reader and can connect to the Square Reader for EMV chip cards and NFC. It also connects to various peripheral devices such as barcode scanners and receipt printers.
- Square Register App. It is a free POS app for iOS and Android mobile devices. It helps sellers accept payments, even without a connection. It can be used to send receipts via email or text message and can help collect customer feedback from digital receipts. It can be used track and manage inventory in real time and print or email sales reports. It can also help adjust taxes, tipping, and discounts. It supports a range of tender types including cash, checks, and gift cards, in addition to credit and debit card payments.
- Square Analytics. The analytics are available through Square Dashboard at Square.com. They help sellers quickly and easily understand how their business is performing.
- Square App Marketplace. It enables sellers to seamlessly integrate third-party apps with Square.
- Square Invoices. Sellers can create custom digital invoices and collect payments securely with Square Invoices.
- Square Gift cards. Square Gift Cards enable sellers to offer, redeem, and track gift cards through Square Register.
- Online Store. Sellers can also create a simple online store with Square Store or build more advanced websites through integrations with companies such as Bigcommerce and Weebly.
- Employee Management. It is a paid upgrade to Square Register that unlocks more advanced features often needed by larger, multi-location businesses. It helps sellers oversee multiple stores from one account, manage employee timecards, and view and act on detailed sales reports that can be filtered by employee, device, or location.
- Square Appointments. It is a online appointment scheduling software. It enables sellers to schedule and accept appointments, manage staff calendars, organize their clients’ information, and view appointment history.
- Square Cash. It is a fast, easy way for anyone to send and receive money electronically. Individuals and businesses can sign up for a Square Cash account using just a debit card and an email address or a phone number.
Square financial services business offerings include:
- Square Capital. Square capital provides merchant cash advances (MCAs) to pre-qualified sellers. Square proactively reaches out to sellers with an offer of an advance based upon their payment processing history. Sellers can use the funds to increase inventory, buy equipment, or open a new location. In return, Sellers agree to make the payments back to Square as a fixed percentage of daily card sales, up to a fixed amount.
- Square Payroll. Square payroll is an easy-to-use payroll service for sellers, optimized for those with hourly employees. It works with Square Register to automatically track employee hours worked.
Square marketing services business offerings include:
- Square Customer Engagement. Square customer engagement software helps sellers engage with their customers and promote their offerings through email marketing. Buyers that have opted in to receive a digital receipt via Square Register can contact the seller about their experience directly from the receipt. Square automatically build customer lists for those who have opted in and organizes them into categories such as loyal, casual, and lapsed. Sellers can then create promotions, announcements, or event invitations to send to different categories of buyers.
- Caviar. Caviar is a courier order management app which facilitates food delivery services to restaurants. Caviar manages the delivery logistics and makes it easy for restaurants to reach new customers and increase sales without additional overhead.
Square Customers

Square target customers are sellers that face challenges with the traditional system of accepting payment cards. Some of the challenges that sellers face with the traditional payments processors are: low acceptance rates; expensive hardware and software; fragmented, difficult-to-use solutions; and complex and opaque pricing.
Square provides the following key benefits to the sellers through its solutions: fast, easy, inclusive sign-up; simplicity; affordability; transparent pricing; fast access to funds; ability to take payments anywhere, anytime.
Most of sellers that use Square services are small businesses. According to U.S. Small Business Administration March 2014 report, there are 30 million small businesses in U.S. Over two million sellers currently use Square payment solutions. Here are some sample business types served by Square:
- Food & Beverages – Bakery, Coffee shop, Restaurant, Food Trucks
- Retail – Apparel, Grocery
- Beauty Professionals – Salon, Spa
- Health & Fitness
- Professional Services
- Home & Repair Services
- Non-profit Organizations
- Leisure & Entertainment Events
- Taxi Services
Square Revenue Sources
Square generates revenues from the following sources:
- Transaction Revenue. Transaction revenue consists of fees that a seller pays to process their payment transactions, net of refunds. Square charges a transaction fee of 2.75% of the total transaction amount for processing card-present transactions and for processing payments with Square invoices. Square charges 3.5% of total transaction amount plus $0.15 per transaction for processing card-not-present transactions, where card details are manually entered. Square selectively offers custom pricing for large sellers.
- Starbucks Transaction Revenue. Starbucks transaction revenue consists of fees paid by Starbucks, net of refunds, to process their payment transactions. Square signed a deal with Starbucks in third quarter of 2012 to process card transactions for all Starbucks-owned stores in United States. In October 2015, Starbucks announced that it will transition to another payment processor and will cease using Square payment processing services altogether before third quarter of 2016. As a result, Starbucks transaction revenue will decrease meaningfully in 2016.
- Software and Data Product Revenue. Software and data product revenue primarily consists of revenue related to services provided through software offerings, or revenue derived through Square Capital and Caviar food delivery services.
- Software as a service includes Square Appointments and Square Customer Engagement. Square provides the use of software for a fee.
- Square Capital provides MCAs in exchange for a fixed amount of future receivables. The difference between the aggregate amount of the future receivables and the cash advance is recognized as revenue.
- With Caviar food delivery services, Square charges restaurants a commission fee based on total food order value. Square also charges consumers a fixed delivery fee per transaction, as well as a service fee which is based on total food order value.
- Hardware Revenue. Hardware revenue includes revenue from sales of Square Stand, Square Readers for EMV chip cards and NFC, and third-party peripherals. Third-party peripherals include cash drawers, receipt printers, and barcode scanners, all of which can be integrated with Square Stand to provide a comprehensive POS solution.
Square Cost Elements

The key cost elements of Square are summarized below:
- Cost of Revenue. Cost of revenue consists of following:
- Transaction Costs. Transaction costs consist primarily of interchange fees set by payment card networks and that are paid to the card-issuing financial institution, assessment fees paid to payment card networks, fees paid to third-party payment processors, and bank settlement fees.
- Starbucks Transaction Costs. Starbucks transaction costs are made up of the same components as the overall transaction costs.
- Software and Data Product Costs. Software and data product costs consist primarily of Caviar-related costs, which include payments to third-party couriers for deliveries and the costs of equipment provided to sellers. Cost of revenue for other software and data products consist primarily of the allocated portion of costs related to third-party data center facilities and depreciation, as well as personnel-related and facilities costs related to customer support.
- Hardware Costs. Hardware costs consist primarily of product costs associated with Square Stand, Square Readers for EMV chip cards and NFC, and third-party peripherals. Product costs include manufacturing-related overhead and personnel costs, certain royalties, packaging, and fulfillment costs.
- Amortization of Acquired Technology. These costs consist of amortization related to technologies acquired through acquisitions that have the capability of producing revenue.
- Operating Expenses. Operating expenses consist of product development, sales and marketing, general and administrative expenses, transaction and advance losses, amortization of acquired customer assets, and impairment of intangible assets. For product development and general and administrative expenses, the largest single component is personnel-related expenses, including salaries and bonuses, employee benefit costs, and share-based compensation. In the case of sales and marketing expenses, a significant portion of expenses is related to paid advertising channels, including online, mobile, email, direct mail, and direct response TV, in addition to personnel-related expenses. Operating expenses also include allocated overhead costs for facilities, human resources, and IT.
Square Gross Payment Volume Analysis 2015
Gross Payments Volume (GPV) is defined as the total dollar amount of all card payments processed by sellers using Square, net of refunds. It excludes card payments processed for Starbucks and Square cash peer-to-peer payments service.
Square processed $35.6 billion GPV in the year 2015. The GPV grew 50% year-on-year.
Square 2015 Revenues, Profits, and Profit Margins
Square generated a total of $1.27 billion revenues in the year 2015. Of these total revenues, Square generated:
- $1.05 billion revenues, 82.9% of the total, as the transaction revenue.
- $142 million revenues, 11.2% of the total, as the Starbucks transaction revenue.
- $58 million revenues, 4.6% of the total, as the software and data product revenue.
- $16 million revenues, 1.3% of the total, as the hardware revenue.
Of the $1.27 billion of Square total revenues in 2015, $897 million were the cost of revenue. This resulted in $370 million of gross profit and a gross margin of 29.2%. Square operating expenses were $544 million. This resulted in $174 million of operating loss and an operating margin of -13.8%. After interest and other non-operating income and expenses and income taxes, Square had a net loss of $180 million and a net margin of -14.2%.









